PCOS (Poly Cystic Ovarian Syndrome) and PCOD (Poly Cystic Ovarian Disease) are two medical conditions associated with ovaries and hormonal imbalance in women during their reproductive age and depict the same symptoms. Studies suggest that 10 percent of Indian women have PCOD or PCOS.
But are PCOD and PCOS the same? The answer is no. Many women are not aware that both are two different conditions and affect their bodies differently. Let’s find out how.
What Is PCOD?
PCOD (Polycystic Ovary Disease) is a medical condition in which the ovaries release many partially mature or immature eggs. It affects women of reproductive age as these immature eggs eventually turn into ovarian cysts. The ovaries swell in this condition leading to increased secretion of the androgen hormone. Women who keep wondering, “what are the first signs of PCOD” must know the symptoms are no less than that of PCOS. It is just the causes and treatment effects that differ!
What Is PCOS?
PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) is a condition of hormonal imbalance caused by the increased production of androgen. This problem also affects women of childbearing age as the high androgen levels lead to the formation of cysts in either any of the two or both the ovaries. Women with PCOS experience abnormal weight gain or obesity, irregularity of periods, infertility and hair loss.
PCOS Prevalence in India
According to the National Library of Medicine, the prevalence of polycystic ovary syndrome in India ranges from 3.7% to 22.5%. While it is difficult to narrow the prevalence more precisely, PCOS varies globally from 2.2% to 26%, according to the National Health Portal. According to the reports presented by the National Health Portal, a survey in South India shows that the prevalence of PCOS in the Southern part of the country ranges from 9.13% to 22.5%.
PCOD and PCOS Common Signs and Symptoms?
It is common for women to start experiencing the symptoms of PCOD and PCOS around the time of their first period, while others discover it when they have gained a lot of unusual weight or have difficulty conceiving. Both are most often associated with the following symptoms:
- Weight gain/Obesity
- Irregular periods/no periods at all/heavy bleeding
- Excessive hair growth on the face and body/hair loss on the head
- Acne and skin patches/darkening (nape, elbows, or groin)
- Depression/anxiety/mood swings
PCOS Vs PCOD: Difference Between PCOS and PCOD
The female body contains two ovaries that release an egg alternately every month and androgens (male hormones). Both PCOS and PCOD affect the ovaries and cause hormonal disruption but in different ways. Let’s learn about the difference between PCOS and PCOD:
1. Meaning
PCOS is a condition in which the ovaries produce excessive amounts of male hormones, and this results in follicular cysts being formed every month, which prevent the release of eggs and lead to anovulatory cycles. PCOD is a condition in which the ovaries contain numerous immature or partially mature eggs that subsequently develop into cysts.
2. Cause
There are many causes of PCOD, including hormonal imbalances, psychological stress, genetics, obesity, and poor eating habits, resulting in a paradoxical condition. PCOS can be caused due to inflammation, hormonal imbalances, and genetic/hereditary conditions.
3. Symptoms
Though many symptoms can seem similar for both conditions, there are different PCOD vs PCOS symptoms as well. Some of the symptoms of PCOD include an increase in body fat, irregular menstrual cycles, hair loss, and infertility. PCOS affects metabolism and can have symptoms like hair loss, hair thinning, baldness, irritability, headache, weight gain, and infertility that may start showing up during adolescence.
4. Occurrence
PCOD affects almost a third of all women worldwide, making it far more common than PCOS found less often in women.
5. Impact on pregnancy
PCOD does not affect fertility in women, making them still capable of ovulating and getting pregnant without much assistance as long as they take prescribed medication. A PCOS woman cannot ovulate regularly, so getting pregnant or having a healthy pregnancy is difficult or at risk.
6. Severity
There is not much severity to PCOD, and it can be managed with changes in lifestyle and dietary habits. PCOS is a more severe condition than PCOD since the entire endocrine system is affected, which can result in cognitive dysfunction and metabolic disorder.
| PCOD | PCOS |
|---|---|
| PCOD is a common condition | PCOS is a more serious medical condition |
| 30% of world women population is affected by PCOD | 0.2% to 2.5% of the world women population is affected by PCOS |
| Hormonal imbalances, psychological stress, genetics, and poor eating habits are the main causes of PCOD | Inflammation, hormonal imbalances, and genetic/hereditary conditions are the main causes of PCOS |
| Weight gain, irregular periods and facial hair growth are some of the symptoms of PCOD | Infertility, obesity & hair loss are some of the symptoms of PCOS |
| PCOD does not affects fertility in women | Having a healthy pregnancy is difficult |
| PCOD doesn’t have any serious complications and it can be managed with changes in lifestyle and dietary habits. | PCOS is a more severe condition than PCOD |
Complications of PCOS and PCOD
The risks associated with PCOS are significantly higher than those associated with PCOD. Following are the PCOD and/or PCOS side effects:
1. Infertility
PCOS is more likely to cause infertility than PCOD because it reduces the frequency of women entering the ovulation phase, making getting pregnant more difficult.
2. Unhealthy pregnancy
As per studies, the chances of miscarriage are three times higher for women with PCOS and the possibility of preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, an abnormally large baby, and premature delivery, which can result in difficult delivery or cesarean delivery.
3. Diabetes
Studies suggest that women with PCOS are more likely to present abnormal glucose metabolisms and lipid profiles, leading to a higher risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
4. Endometrial cancer
In women with PCOS, late ovulation causes the endometrium (uterine lining) to thicken and may therefore increase the risk of endometrial cancer.
5. Metabolic syndrome
The health risks associated with PCOS include elevated blood sugar levels, high blood pressure, and low cholesterol and triglycerides, all of which can increase cardiovascular risks as well.
6. Obesity
Because PCOS patients are insulin resistant and insulin does not function properly, they tend to gain weight and become obese.
7. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
PCOS may cause the liver to become enlarged due to severe inflammation and fat accumulation.
8. Depression
Symptoms of hormonal imbalance can result in depressive symptoms, mood swings, irritability, and behavioural changes in women with PCOS and PCOD.
9. Sleep Apnea
A female with PCOS is at greater risk of this condition, which is characterised by repeated breathing interruptions during the night. This condition is more common among overweight females.
How to Diagnose PCOS and PCOD
PCOS and PCOD cannot be definitively diagnosed without discussing with a healthcare professional your medical history, including your menstrual cycle and weight changes, and other common symptoms. PCOS is diagnosed when women exhibit two of the three main symptoms - high androgen levels, irregular periods, or cysts around the ovaries, which can further be confirmed with lab tests, physical tests, and sonograms.
1. Pelvic test
During this test, your doctor will look for masses, growths, and other abnormalities in your reproductive organs by inserting gloved fingers into your vagina and feeling around.
2. Ultrasound
Sound waves are used to assess your ovaries and uterus for problems, such as abnormal follicles. In this procedure, the doctor briefly inserts an ultrasound device in your vagina, causing the device to produce an image of your ovaries which helps him check for cysts in them and how thick your uterine lining is.
3. Blood test
Obtaining blood samples enables you to check your cholesterol, insulin, triglyceride, and blood sugar levels and check for higher than normal levels of male hormones, all of which are associated with PCOS.
PCOD and PCOS Treatment
There are several concerns addressed by PCOS treatment, including infertility, hirsutism, acne, and obesity, which are only designed to reduce these symptoms and prevent them from worsening. This is done through various medications and procedures.
- Treatment of hormonal imbalance and insulin resistance by taking prescribed medication to regulate the menstrual cycle
- Administering oral medicines and injections to incite ovulation (both in terms of quality and quantity)
- Fertility drugs are used to treat infertility
- Excessive hair growth must be controlled through medication or surgery
- A skincare regimen for acne and pigmentation
- Laparoscopic ovarian drilling is used when hormonal treatment for PCOS does not produce satisfactory results
Home Remedies to Control PCOS and PCOD
Both PCOD and PCOS may be controlled with the aid of using lifestyle and nutritional changes; however, PCOS remedies may also require vast care. Following are a few ways you can improve your condition.
1. Weight loss
Losing weight by following a low-calorie diet and exercising frequently can help to deal with PCOS and PCOD. As per studies, women with PCOS can lose weight by doing moderate-intensity exercise for 30 minutes three times a week. In addition, it increases the effectiveness of medication recommended for PCOS, leading to improved ovulation and insulin levels.
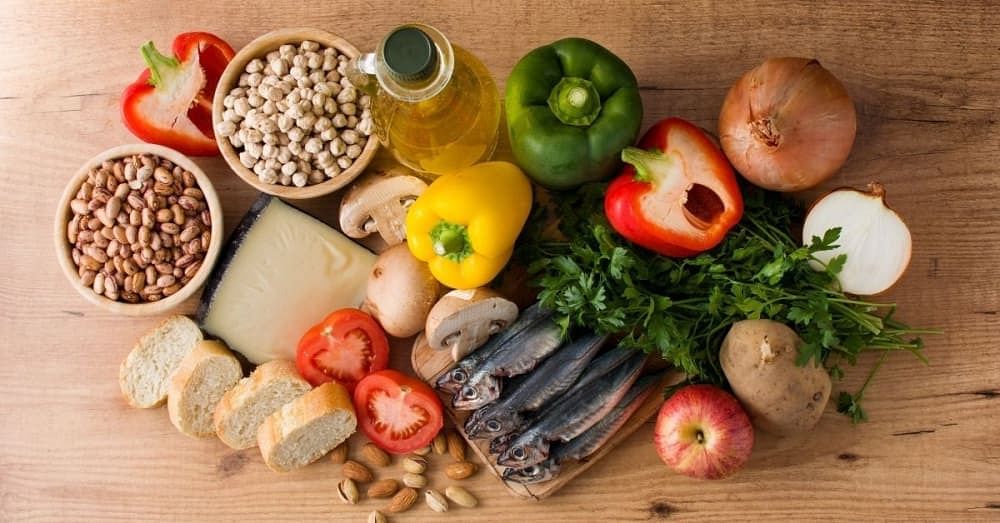
2. Healthy diet
The symptoms of PCOS and PCOD can be controlled, and hormonal imbalances can be improved by following a healthy diet and regular workout routine. To avoid PCOS-induced insulin resistance, you should limit intake of starches, sugars, and highly refined carbs and increase intake of high-fibre foods and veggies, nuts, and olive oil.
3. Regular workout
By exercising, you lower your blood sugar levels. Exercise and increasing daily activity may help manage weight, prevent diabetes, and treat insulin resistance in PCOS.
4. Sleep hygiene
A sleep hygiene program is a system of behavioural and environmental interventions designed to encourage healthy sleeping and was developed to treat sleep disorders. As per studies, modifying sleep behaviour is one of the most important lifestyle changes that can be made to improve PCOS treatment outcomes. This can be done by fixing a sleep schedule and avoiding several things like caffeine, smoking, bed-time snacking and screen time, daytime naps.
PCOS vs PCOD – Diet
While no particular food item you consume in your diet can cause PCOD or PCOS, maintaining a healthy and balanced diet helps prevent and minimise both PCOS and PCOD. Since weight gain is a significant symptom of both PCOD and PCOS, keeping a healthy diet helps to prevent obesity or weight gain, which controls the conditions.
Some tips to keep in mind for both PCOS and PCOD are:
- Stay away from carbohydrate-rich foods.
- Avoid foods filled with starch and sugar that attack insulin resistance.
- Add fresh fruits and vegetables to your diet as they are low in glycemic index and restrict weight gain.
- Use olive oil for food preparation.
- Avoid packaged or processed foods to lower the risk of hypertension.
Making these and other healthy changes to your diet can reduce many symptoms like weight gain, acne, hair fall, etc. Since a change in your regular diet can show tremendous improvements in your PCOD or PCOS condition, so you must adapt to a healthy diet.
When to See a Doctor
If you are experiencing any PCOD or PCOS symptoms such as heavy bleeding, infertility, irregular periods, heavy hair fall, sudden weight gain, acne, etc., you must visit a doctor to confirm whether you have PCOD or PCOS condition to control it as early as possible.
Summing Up on PCOS Vs PCOD
Maintaining good health is essential to prevent as well as a treat hormonal disturbances and conditions. By following the prescribed treatment and using home remedies, you can easily control PCOS and PCOD on your body.
It's important to follow the instructions of your doctor to bring balance to your life while making all necessary lifestyle changes. An important part of treating PCOD and PCOS is to diagnose them in a timely fashion and to take steps that can ease the difficulty of the situation and facilitate the journey towards recovery.
FAQs
Which Is More Harmful PCOS or PCOD?
PCOS is more harmful than PCOD. PCOD is not even considered a disease entirely and can be controlled and nearly cured with a proper diet and exercise regime. PCOS is a serious condition and needs treatment by consulting a doctor as it is a metabolic disorder.
A hormonal imbalance may result from PCOS if there is excessive production or deficiency of a hormone. PCOD is a medical condition caused by hormonal imbalance, which is a symptom itself.
Can Women Get Pregnant When They Have PCOD?
Having PCOD or PCOS does not preclude women from getting pregnant. However, when it comes to PCOD, getting pregnant may be normal, but that is not the case in PCOS. The risk for certain complications in pregnancy is higher for PCOS women. PCOS-affected mothers are more likely to have preterm or stillbirth or die shortly after birth.
However, if you do want to get pregnant and avoid all of the complications, you can seek all the assistance you want from your healthcare professional. Modern medicine has made it possible for women to aspire to a healthy pregnancy through drug-induced ovulation, surgery, or IVF (In Vitro Fertilisation).
Can You Have Weight Gain in PCOS or PCOD?
Yes, you can gain weight in Pcos or Pcod. Insulin resistance is thought to be the main cause of weight gain in women with PCOS and PCOD. When cells inside the body are resistant to the insulin produced by the pancreas, the pancreas must produce more insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels, which leads to weight gain and increased production of androgen. In this situation, insulin resistance increases, as do symptoms and weight gain.
Some other reasons associated with weight gain in PCOD and PCOS are stress, anxiety, lack of sleep, overeating, etc.
Can PCOD Be Cured Permanently?
It's not possible to cure PCOD completely, but treatment options are. As medical science progresses rapidly, you have access to a variety of treatments that you can use to cope with symptoms you may experience.
To lead a healthy and happy life, women need to not get scared and give up all hope because, with the right medical treatment and lifestyle changes, they can live a normal life as well as anyone else.
References
- Maryam Bahman, Homa Hajimehdipoor, October 2018; The Importance of Sleep Hygiene in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome from the View of Iranian Traditional Medicine and Modern Medicine - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6202781/
- A Gambineri, R Pasquali, February 2004; Type 2 diabetes and the polycystic ovary syndrome - https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14973409/
- R.Vidya Bharathi, Swetha, December 2017; An epidemiological survey: Effect of predisposing factors for PCOS in Indian urban and rural population - https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1110569016301510